Our health, the environment, and even our prosperity may suffer if waste management is not done properly. Great methods can be found all over the world, and effective examples can aid in the development of new reuse and recycling concepts. In this article, you will learn everything you need to know about a waste management system, including an introduction to waste management, waste disposal techniques, tools for reducing waste, tips for conducting efficient waste audits, and additional resources for helping your company comply with environmental laws.

Things we covered for you
What is Waste Management?
Waste Management refers to the processes that we use to manage waste.
Read: Homemade Toilet Cleaner Recipes: Effective and Eco-Friendly Solutions
This includes gathering, moving, disposing of or recycling waste materials that are the result of human activity. The method an organisation employs to dispose of, reduce, reuse, and prevent waste is also known as a waste management system.
Recyclables, compost, waste to energy, landfills, incineration, bioremediation, and waste minimization are all potential waste disposal techniques.
All waste types, including hazardous, industrial, and household waste, are included in waste management. Additionally, waste can be solid, liquid, or gas, and each of these has a unique management and disposal process.
Reducing the amount of trash that is dumped in landfills is the entire point of waste management. The opposite should be true—waste should be viewed as a resource.
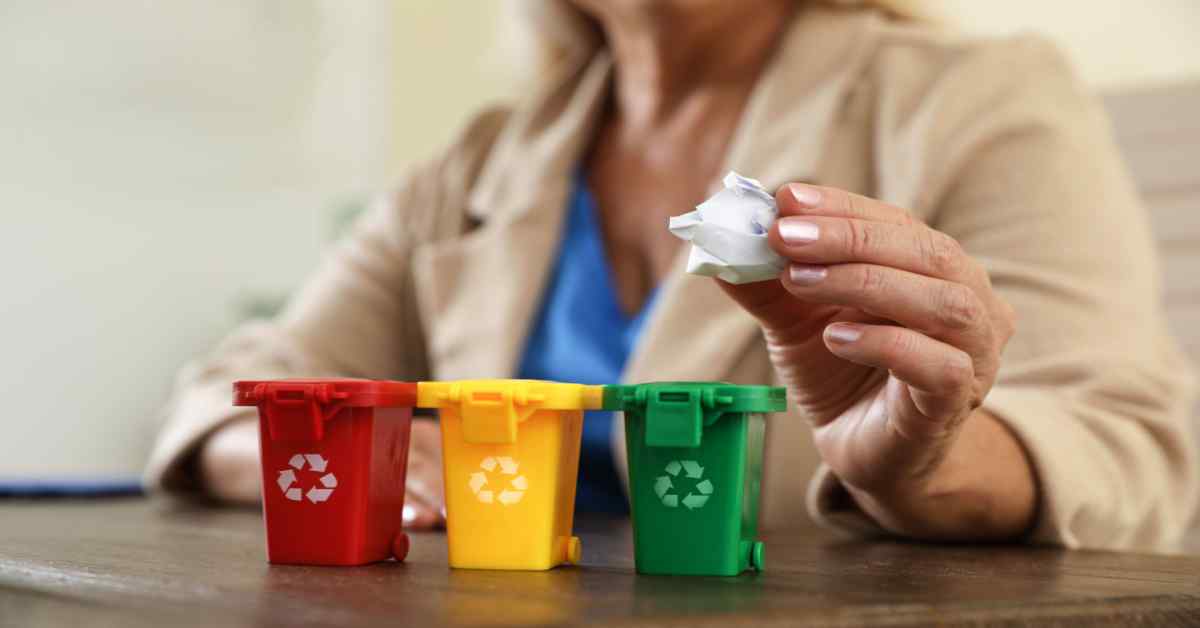
Different Waste Segregation Techniques You Can Use
Waste segregation refers to the separation of dry and wet waste. Wondering what is wet waste or dry waste for instance? The dry waste consists of metals, glass, and wood-related products. Wet waste generally refers to natural waste that is usually produced by restaurants and is heavy due to moisture. Waste sorting and waste segregation are distinct processes.
Examples of Dry Waste: Paper, cardboard, metal, food, styrofoam, glass, plastic, rubber, and packaging material.
Examples of Wet Waste: Food scraps, tea leaves, coffee grounds, egg shells, meat and bone fragments, and other biodegradable kitchen waste, along with leaves and flowers.
Investigating the 3Rs of Waste Management: Reduce, Reuse, and Recycling
Each of us must contribute to preventing as much waste away from landfills as we can. Utilizing the 3 Rs of waste management—Reduce, Reuse, and Recycle—is one way to carry out that plan.
- Reducing means minimising the amount of waste we produce.
- To reuse something is to come up with new ways to use something that would otherwise be thrown out.
- Recycling is the process of converting waste materials into new, useful materials, such as used plastic milk jugs recycled to make benches and bins, etc.
Apart from these steps, make sure you don’t dump your waste just anywhere. As responsible citizens, make sure your residential waste is only handed to the agency responsible for garbage collection in India.
Read: Move Out Cleaning Guide: Things To Keep In Mind
Wondering how to find out about the methods of waste management in my locality? Just make a simple google search with the name of your locality and you will find out the agency responsible.
The Various Methods of Waste Disposal and Management
Here are some of the most accepted global techniques for waste management:
1. Landfill
The most common waste disposal technique used today is tossing daily waste and garbage into landfills.
Burying waste in the ground is the primary focus of this waste disposal process. The waste that cannot be recycled or reused is separated during this process and then distributed as a thin layer in low-lying areas all over a city. Each layer of trash is followed by a layer of soil.
However, after this procedure is finished, the area is deemed unfit for building construction for the following 20 years.
It can only be used as a park or a playground instead. In essence, landfills are sizable holes dug into the earth that are intended to hold trash.
However, similar to combustion, it isn’t the preferred waste management approach because these locations are known to have numerous negative effects on the environment and human health.
For instance, toxic substances and chemical leaks can seriously harm the environment by contaminating the nearby soil. As landfills are filled, methane can also be produced, a highly dangerous greenhouse gas that is 28 times more potent than CO2.
Read: Amazing New Homemade Cleaning Aids for You to Try
2. Incineration
Incineration, also referred to as combustion and thermal treatment, is a waste-management technique that involves igniting solid waste at extremely high temperatures to produce heat, gas, and steam.
The exhaust gases from this process are treated before being released into the environment because they could be toxic. The amount of waste is 90% lessened by this process. Even though most materials can be disposed of in this manner, it is frequently the most convenient way to handle hazardous waste.
Occasionally, the heat produced is used to create electricity. However, because this process produces greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide, some people believe it is not entirely environmentally friendly.
3. Compaction of waste
Cans and plastic bottles that are waste are compressed into blocks and sent to be recycled. This process makes transportation and positioning simple by preventing metal oxidation and lowering the need for airspace.
4. Biogas Production
Anaerobic digestion, the process by which bacteria break down organic materials such as plant and animal products without the presence of oxygen, results in the production of biogas. Waste that decomposes over time is sent to biodegradation facilities, including food waste, animal waste, and organic industrial waste from the food packaging sector.
Read: Vinegar for Cleaning: Tips, Types, and Tricks [Guide]
They are degraded in bio-degradation facilities with the aid of bacteria, fungi, or other microbes before being converted to biogas. In this instance, the organic matter provides the microorganisms with food. Degradation may occur either anaerobically or aerobically (with oxygen) (without oxygen). This process produces biogas, which is used as fuel, and the leftover material is turned into manure.
5. Composting
Composting is a simple and organic bio-degradation process that converts organic wastes, such as plant remains, garden waste, and kitchen scraps, into nutrient-rich food for your plants. With time, all organic materials deteriorate.
One of the main organic wastes we discard each day includes food scraps, yard waste, and other things. These organic wastes are first buried beneath several layers of soil, where they are then allowed to decompose due to the action of bacteria and fungi. As a result, nutrient-rich manure is produced.
Additionally, this procedure makes sure that the soil’s nutrients are replenished. Composting improves the soil’s ability to retain water in addition to enriching it. It is the best substitute for chemical fertilisers in agriculture.
6. Vermicomposting
Vermicomposting is a naturally occurring bio-oxidative decomposition process that takes place in mesophilic conditions and is further aided by the biochemical activity of microorganisms.
By-products of digestion that the worms excrete into the soil make it rich in nutrients, which promotes the growth of bacteria and fungi. Additionally, it is a lot more efficient than conventional composting.
7. Recycling
Recycling makes it possible to repurpose waste materials and create new goods. This not only conserves natural resources, but it also uses less energy, costs less to make new materials, and emits fewer greenhouse gases.
The Impact of Poor Waste Management
Surface water, groundwater, land, and the air may all become contaminated as a result of improper waste management.
One-fourth of the world’s waste is produced in East Asia, while South Asia and Sub-Saharan Africa are the two regions where waste production is expanding at the fastest rate.
For instance, improper handling occurs when waste is improperly burned, illegally dumped along roadsides, dumped in wetlands, dumped in lakes and streams, dumped in the woods, or burned. Waste that has already harmed the environment can:
- cause possible risks to human health
- harm or destroy plants and animals
- Natural resources are harmed.
- disease outbreak
In addition, unsightly waste accumulations can harm India’s natural beauty, lower society’s quality of life, depreciate the value of nearby homes, harm tourism, and increase municipal cleanup costs.
Poor waste management is polluting the world’s oceans, filling up drains and causing flooding, spreading diseases, escalating respiratory issues from incinerating, harming animals that unknowingly consume waste, and hindering economic development, such as tourism. Municipal solid waste is produced on a global scale of more than 2 billion tonnes annually. Without immediate action, this will rise over the following thirty years by almost a third, to 3.4 billion tonnes.
High-income nations produce more than one-third of the world’s waste even though they only make up 16% of the world’s population.
The Benefits of a Waste Disposal System
Waste management lessens waste’s negative effects on the environment, human health, and other factors.
Additionally, it can aid in the recycling or reuse of materials like paper, canisters, glass, and others. Several types of waste management involve the elimination of hazardous or toxic materials that are solid, liquid, gaseous, or vapour.
When talking about waste management, there are a lot of things to keep in mind, including disposal techniques, recycling techniques, avoidance and reduction techniques, and waste transportation.
Waste management entails handling both solid and liquid waste. It also provides a range of options for recycling items that aren’t considered trash during the treatment.
Waste Management Colour Coding
Due to a significant rise in population, urbanisation, and industrialization, waste generation and disposal are major issues today. Landfills are yet another issue for waste disposal because of their small size and ongoing decline.
The risk to the environment, social order, and human health is reduced by waste segregation. Sorting and separating waste for recycling and convenient disposal is known as waste segregation. Red, blue, green, and other coloured dustbins were used to accomplish this.
Every person should act because the government cannot handle it on its own. It will be challenging to manage all the waste when it is collected together, so the idea of using coloured trash cans was promoted to make recycling simple. The trash that each of these dustbins gathers is different.
Red Trash Can
It is employed for non-biodegradable waste. Since these wastes cannot be recycled, it is also referred to as rejecting dustbins. It is typically located in hospitals and is used to collect biomedical wastes, which must be disposed of carefully and include needles, surgical knives, body fluids, cotton dressings, pop casts, tissues, and sanitary napkins.
Infected needles can spread diseases like HIV, Hepatitis B, and C if they are not disposed of properly. Wastes that are hazardous and non-hazardous are both presents. These waste materials are taken for incineration because they cannot be recycled.
Green Trash Can
Wet and biodegradable waste is used in it. As it holds waste from the kitchen, plants, and animals, it is also referred to as an organic bin. These wastes include rotten eggs, fruit and vegetable peels, tea bags, used tea powder, leftover food, garden waste, and coconut shells. The kitchen garden uses organic waste as manure to grow vegetables.
Farmers use the remaining waste for manure and composting, which helps to increase the soil’s fertility. Some of these wastes are sterilised and fed to animals. Composting reduces this waste to zero waste. Occasionally, when plastic wrappers are combined with this trash and unfortunate animals eat it, the animal perishes.
So, proper care should be taken when disposing of waste. When materials fall into dustbins, it can be challenging to distinguish between them. For instance, if a biscuit packet contains biscuits, the biscuits should go in the green trashcan and the biscuit wrapper should go in the blue trashcan. Food that has gone bad or expired needs to be taken out and thrown away.
Only when there are excessive amounts of these wastes do they become a problem. This organic matter emits a foul odour that can cause human diseases when breathed in.
Blue Trash Can
Dry, non-biodegradable waste is used for it. In other words, if the paper is dry, it goes in a blue trash can, and if it’s wet, it goes in a green trash can.
After removing and rinsing the liquid wastes, the plastic wrappers and covers are dried before being discarded in the trash. This waste is classified as non-biodegradable waste because microorganisms cannot decompose it; therefore, it must be recycled. They harm the environment and cause pollution if improperly disposed of. This trash can should be used to dispose of items such as plastic, aluminium cans, polystyrene, newspapers, paint, aerosol cans, lights, broken bulbs, glass bottles, plastic bottles, gift wrap, cards, cardboard, thermal coal, and tetra pack packaging.
These wastes are recycled and reused, which reduces the amount of trash that needs to be disposed of in landfills and lessens the impact on groundwater levels. Other wastes, such as electronic devices in iron boxes, mobile phones, TVs, computers, led bulbs, CDs, and pen drives, should be turned in at e-waste collection facilities rather than being thrown away.
The waste sorters’ job is made simpler and more effective. As a result, waste can be reused and decreased.
The governance and administrative cost of Waste management is high.
But proper waste management makes financial sense—Uncollected waste and improper waste disposal have negative effects on both human health and the environment. Solid waste management is essential for creating cities and communities that are sustainable, healthy, and inclusive in a time of rapid urbanisation and population growth.
To stop that trend, we already know what needs to be done. All levels of society must simply act immediately. Waste management must be done sustainably for everyone. The moment is now to take action.
If you are trying to find a new home in a different city or a different part of your city, consider using NoBroker Rental Services. NoBroker’s rental listings can help you understand if the locality has any waste management services available. You can also arrange for a relationship manager who will take care of all your rental-related worries.
Download the NoBroker App now for finding the perfect rental home.
Home Cleaning Service in Top Cities in India
Frequently Asked Questions
Ans. Waste management includes the routine collection, transportation, processing, disposal, or recycling of various waste materials, as well as monitoring. These services have the potential to save your company a sizable sum of money while also protecting the environment.
Ans. In addition to lowering greenhouse gas emissions, proper waste removal aids in enhancing the quality of the air, water, and environment. It minimises the number of resources that must be extracted, as well as the pollution and energy use involved in producing new materials.
Ans. They are yellow, black, and white trash cans, yes. Black dustbins are used for e-waste, white dustbins are used for soft plastic recycling, and yellow dustbins are used for mixed recycling materials.
Ans. For door-to-door collection, the BBMP operates a fleet of 4646 Auto Tippers (Primary Collecting Vehicles). To ensure 100% door-to-door collection, 618 compactors were used to collect and transport waste from secondary collection points (Transfer Stations).
Ans. The management of waste at every stage, from generation to disposal, is referred to as garbage disposal. Government cannot bear all of the burdens on its own. To keep our surroundings clean, we should assist the government in its efforts.